

The controlling factors in the Geopier design are the magnitude of stress applied to the RAP element, the stiffness of the element, the stiffness of the matrix soil, and the predicted settlement of the improved soil. WHAT IS THE MINIMUM AREA RATIO FOR A FOOTING SUPPORTED BY RAP SYSTEMS? The chains allow the stone to flow into the pier when the mandrel is raised and act to form a “fist” to compact the stone when the mandrel is lowered.Ħ.

The mandrel is then lowered 2 ft to compact the stone – creating a 1 ft compacted stone lift. The mandrel is raised 3 ft to allow stone to flow out into the pier. Stone is then placed through the center of the mandrel and compacted using a chain system inside the lower end of the mandrel. Piers are constructed by pushing a hollow mandrel into the ground which will displace the soil and act to temporarily case the shaft. RAP elements can be installed below the ground water table using the Impact displacement system. CAN RAP ELEMENTS BE INSTALLED BELOW THE GROUNDWATER TABLE? The length of a RAP element can also be evaluated by an on-site modulus test, which confirms that the stress is being distributed as designed.ĥ. This is why piles are required to go much deeper than RAP elements.
#Safety factor for spot pier footings plus
Whereas a deep foundation such as a pile or drilled shaft typically derives a significant majority of its capacity in end bearing plus the bond zone between the pile and soil once it hits a dense layer. The applied stress is relieved in friction along the Geopier profile and not in end bearing. The systems are designed to improve the soil within a zone beneath shallow footings where the stresses are the highest. Rammed Aggregate Pier® (RAP) elements do not need to extend to a firm-bearing layer like a pile foundation. DO THE RAMMED AGGREGATE PIER® ELEMENTS NEED TO EXTEND TO A DENSE SOIL LAYER OR ROCK? When organic or peat soils are encountered, cement treated aggregate can be used to stiffen the pier in the organic zone or throughout the entire pier, if needed.Ĥ. Geopier systems can be used to improve very soft to stiff clay and silt, organic silt and peat, loose to dense sand, mixed soil layers, uncontrolled fill, and soils below the ground water table. IN WHAT TYPE OF SOILS SHOULD I BE USING GEOPIER SYSTEMS? Geopier systems are also used to provide liquefaction mitigation, uplift resistance and increased resistance to lateral loads.ģ. GP3 and Impact elements are used to support commercial, industrial, transportation and residential applications, including buildings up to 20 stories tall, industrial tanks, heavily-loaded warehouse floor slabs, MSE walls and embankments, and other transportation structures.
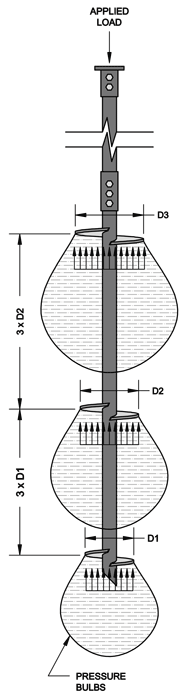
GP3 and Impact systems are alternatives to overexcavation and replacement of weak soils or fills, and deep foundation systems such as piles or drilled shafts. WHAT ARE TYPICAL APPLICATIONS FOR GP3 AND IMPACT SYSTEMS? Due to this high degree of vertical compaction and lateral confinement, the Geopier element provides stiffness that can control settlement of structures very efficiently.Ģ. This means that the lateral stresses of the soil can be as much as 2 to 3 times greater than originally imparted by the soil. The lateral stress in the matrix soil surrounding the Geopier element approaches Kp, the coefficient of passive earth pressure. The high-energy impact compaction imparted on the aggregate within the Geopier element also produces significant lateral pre-straining and pre-stressing of the adjacent matrix soils. Geopier Rammed Aggregate Pier® (RAP) systems consist of a very stiff, vertically rammed, compacted aggregate shaft placed within the soil needing improvement. HOW DO THE GEOPIER RAMMED AGGREGATE PIER® SYSTEMS (GP3® SYSTEM AND IMPACT® SYSTEM) WORK?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
